Mora Tapinella ID: Guide & How To Identify!
Is it possible that a single identifier could unlock a hidden world of fungal complexity, revealing the secrets of the forest floor and beyond? The answer lies within the microscopic world, and it's a world where Mora tapinella id serves as the key, unlocking a treasure trove of scientific and ecological knowledge.
The designation Mora tapinella id might seem like a simple string of characters, a technical term relegated to the dusty corners of scientific literature. But in reality, it represents much more. It is the gateway to understanding a fascinating species of fungus, a key player in the intricate ecosystem of forests across the globe. This identifier allows us to track, study, and appreciate the unique characteristics, distribution, and ecological significance of a specific type of bracket fungus. By understanding Mora tapinella id, we are not just studying a fungus, but also uncovering the stories held within the trees, the soil, and the very air around us.
| Characteristic | Details |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Mora tapinella |
| Common Name(s) | Bracket Fungus, Brown Rot Fungus (depending on context and location) |
| Taxonomic Classification | Fungi > Basidiomycota > Agaricomycetes > Polyporales |
| Habitat | Primarily found on hardwood trees, often causing decay. Prefers damp environments. |
| Distribution | Variable, depends on the specific identification. Known from Europe, North America, and possibly other regions. |
| Ecological Role | Decay wood; contributes to nutrient cycling within the ecosystem. A decomposer. |
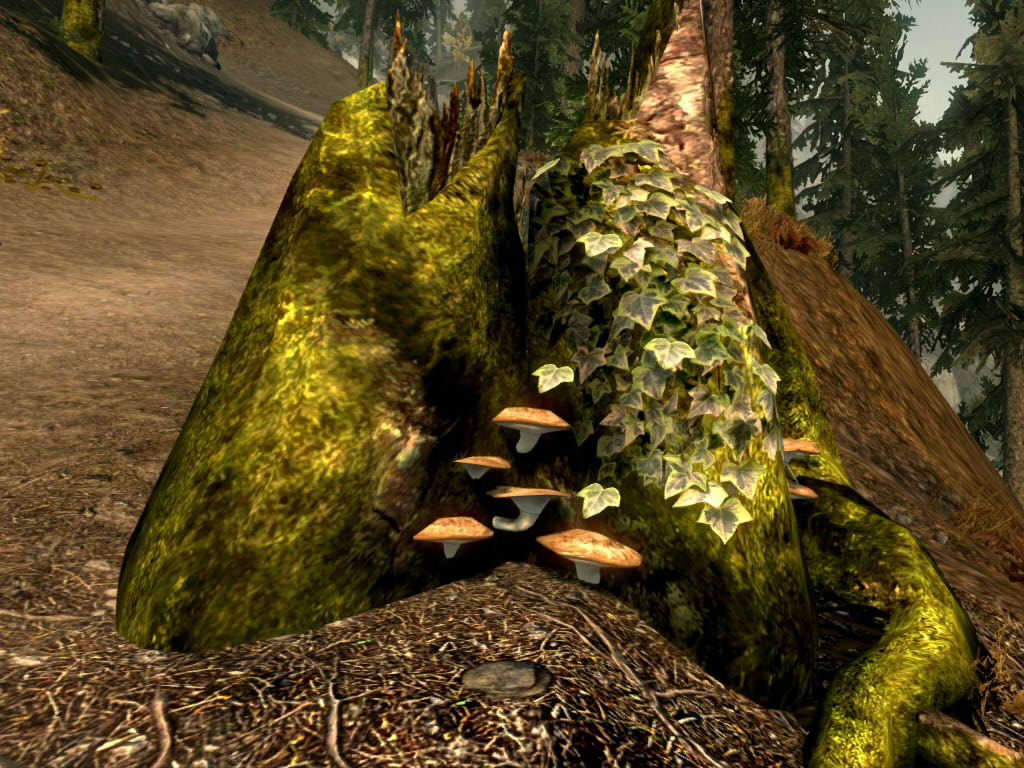
| Morphology | Bracket-shaped fruiting bodies (basidiocarps) that are typically brown or reddish-brown in color. Can be shelf-like or fan-shaped, and often grow in overlapping clusters. |
| Impact on Trees | Causes brown rot, which weakens the wood structure of infected trees. This can lead to structural failure. |
| Identification Characteristics | Color, shape of the fruiting body, pore structure (underside of the bracket), and the type of wood it is found on. Microscopic analysis of spores is often required for definitive identification in some cases. |
| Edibility | Generally considered inedible due to its tough texture. |
| Other Considerations | Consider the host tree species and geographical region when trying to identify this fungus. Molecular techniques (DNA analysis) are often employed to confirm its presence. |
| Further Reading (Reference) | MykoWeb: Mora tapinella |
The study of Mora tapinella and its identification, as represented by " Mora tapinella id", requires an understanding that extends beyond simple classification. It demands a focus on the ecological context the specific trees it infects, the environmental conditions that foster its growth, and the broader impact on the forest community. This holistic approach is essential for gaining a complete picture of its role. The identification of specific species is crucial in understanding the impact on forest ecosystems. Accurate identification allows foresters to assess the health of trees, manage forests sustainably, and mitigate potential hazards. Research into this species is constantly evolving, revealing more about its life cycle, genetic diversity, and potential interactions with other organisms.
One of the key aspects of understanding Mora tapinella id is its impact on the trees it colonizes. This fungus is known for causing brown rot, a type of wood decay that breaks down the cellulose in the wood, leaving behind a brown, crumbly mass. This decay weakens the tree's structural integrity, making it vulnerable to wind, storms, and other environmental stressors. The rate of decay and the extent of damage can vary depending on the tree species, the environmental conditions, and the specific strain of the fungus. Understanding these variables is vital for predicting the potential risks posed by Mora tapinella and developing effective management strategies.
The identification process, as encapsulated in Mora tapinella id, often begins with visual inspection. The bracket-shaped fruiting bodies, with their characteristic brown or reddish-brown coloration and shelf-like or fan-shaped form, are a key initial clue. The presence of pores on the underside of the fruiting body is another important characteristic. However, visual identification alone can sometimes be challenging, as the appearance of Mora tapinella can vary depending on the environmental conditions and the stage of its development. For definitive identification, mycologists often rely on microscopic analysis of spores, which can provide critical information about the species.
Beyond visual and microscopic analysis, molecular techniques, such as DNA sequencing, are increasingly used for accurate identification. These techniques allow scientists to analyze the genetic material of the fungus, confirming its species and identifying any genetic variations. This is especially important when dealing with closely related species that may share similar physical characteristics. The use of molecular techniques is not just for the definitive identification of species. They also offer valuable insights into the genetic diversity within the Mora tapinella population, which can influence factors such as its virulence, its ability to spread, and its response to environmental changes.
The study of Mora tapinella id and its broader ecological context has numerous practical applications. Foresters and arborists rely on accurate identification to assess the health of trees, implement effective management strategies, and mitigate the risks associated with fungal infections. Identifying and monitoring the spread of the fungus is essential for preserving the structural integrity of forests, preventing tree failure, and safeguarding public safety. Additionally, an understanding of Mora tapinella can inform sustainable forestry practices, helping to promote healthy forests and biodiversity. Proper management of the trees requires a detailed study of the conditions that enable the growth of the fungus and what measures can prevent or slow it.
The research into Mora tapinella is ongoing. Scientists are continuously working to learn more about its life cycle, its interactions with other organisms, and its role in the ecosystem. New discoveries are frequently being made, revealing the complex interplay of factors that influence its behavior and its impact on the environment. Some research focuses on exploring the genetic diversity within Mora tapinella populations. Studying the host range, which is the range of tree species that the fungus can infect, helps determine its potential spread and impact. Investigating potential control measures, such as biological control agents or targeted treatments, is another area of active research.
The ecological role of Mora tapinella is multifaceted. As a decomposer, it plays a vital part in nutrient cycling within the forest ecosystem. By breaking down dead wood, it releases essential nutrients back into the soil, where they become available for other organisms. In this process, it acts as a critical link in the food chain, supporting the growth of other fungi, insects, and microorganisms. The impact can vary depending on the forest type, and species-specific host preferences. The fungus influences the overall biodiversity and the health of the entire ecosystem, as it plays a major role in the decomposition and nutrient cycling processes.
The distribution of Mora tapinella is also an important area of study, as it provides insights into the environmental factors that support the fungus. The funguss geographic range, including its presence and abundance in different regions, provides critical clues about the climate, tree species, and environmental conditions that influence its survival. Studying its distribution helps scientists predict potential spread, identify vulnerable areas, and develop effective management strategies. Information on its distribution may indicate changes to forests due to climate changes. Tracking the range also helps manage the trees infected by the fungus, which may provide a long term solution.
The broader significance of understanding Mora tapinella id is that it represents a powerful example of the interconnectedness of life. By studying this seemingly simple fungus, we are gaining insights into the intricate web of relationships that govern the forest ecosystem. We learn about the roles that different species play, the impact of environmental changes, and the importance of preserving biodiversity. The study reminds us that all organisms are interconnected. Through learning more about the role and characteristics of the fungus, we are learning more about the forest. The forest's complexity is tied to the understanding of this simple fungus.
Further research and identification of Mora tapinella id requires a multi-disciplinary approach, integrating expertise from mycology, forestry, molecular biology, and ecology. This collaboration is essential for developing a comprehensive understanding of the fungus, its impact, and its role in the environment. Continued studies may reveal new species and varieties, further expanding our understanding of the fungal world and its impact. It could also help to understand how climate change and human activity can affect Mora tapinella and the forests it inhabits. Such insights can lead to the development of strategies to mitigate the impact of diseases and protect forest ecosystems.
In conclusion, " Mora tapinella id" is more than just a scientific label. It represents a gateway to understanding the complexities of fungal ecology, its role in forest health, and the importance of conservation efforts. Through continued research and the integration of diverse scientific disciplines, we will further unlock the secrets held within Mora tapinella, contributing to the long-term health and sustainability of our forests.